Today, more and more growers are installing LED lighting instead of traditional HID and T5 fluorescent lights. LEDs emit less heat than HID light sources, which means that LED grow lights can be placed differently to the canopy than traditional grow lights. It’s also important to understand how the optimal grow light distance affects the different stages of plant growth.
This article outlines the different lighting needs of various plants, including cannabis, based on their growth stage. It also discusses how to determine the proper distance of LED lighting from the plant canopy to nourish plant growth, and the importance of PPFD (PAR) and other popular grow light terms.
How to Measure Light for Plant Growth
Let’s quickly define PAR and PPFD. PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation) describes the portion of the visible light spectrum that plants “see” and use for photosynthesis (400nm-700nm). PPFD (Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density) measures the amount of light (PAR) that a plant receives over time. PPFD represents the light density that a plant receives over time, expressed in micromoles [photons] per square meter per second.
One way to visualize PPFD is to imagine the sun “pouring” light onto a plant’s leaves. As the sun shines its rays on plants, their leaves are collecting energy. PPFD is a measurement of the amount of light (photons) that the sun "pours" onto plants over time. PPFD is an important metric because it helps growers accurately measure light intensity for photosynthesis at the canopy level. It's also important because lights too close to the canopy can cause burning, fading, stunted growth, or discoloration.
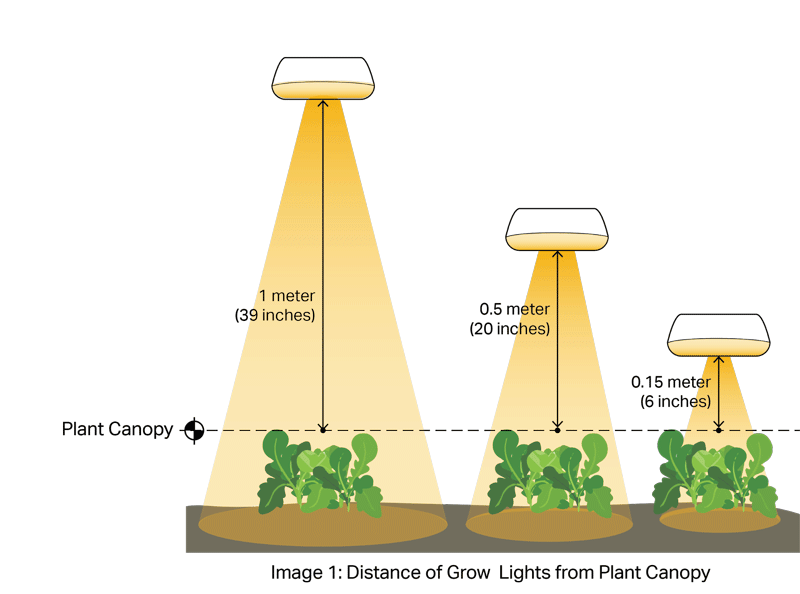
LED Grow Light Distance Chart
LED plant light distance Plant leaf height (m/inch)
| Light intensity (Lux)
| Center point PPFD / PAR (μmol/m-2/s-1)
| Lamp radiant area (m² / ft2)* |
2m / 79 inches | 955lx | 670 | 7.6m2 / 81.8ft2 |
1.5m / 59 inches | 1692lx | 1170 | 5.0 m2 / 53.8ft2 |
1m / 39 inches | 3663lx | 1670 | 3.0 m2 / 32.3ft2 |
0.5m / 20 inches | 12,500lx | 2170 | 1.5 m2 / 16.1ft2 |
0.2m / 8 inches | 50,300lx | 2670 | 0.5 m2 / 5.4ft2 |
Table 1: Distance of LED Grow Lights from Plant Canopy (600W LED Grow Light)
* Coverage will vary depending on the grow light used. The LED grow lights shown here do not use lenses to direct the distribution of light.
Table 1 shows the performance of a 600W LED grow light at different distances from the plant canopy. It outlines the light intensity (lux), provides PPFD (μmol/m-2/s-1 or micromoles per square meter per second), and also shows the “light footprint” or canopy coverage. The intensity, PPFD/PAR, and “light footprint” all change as the distance of the light from the plant canopy increases or decreases.
Table 1 also highlights how changing the distance of the same 600-watt LED light changes the light intensity and “light footprint” or canopy coverage received by the plant. Light intensity increases when the light source is located closer to the canopy. Generally, grow lights should be mounted closer to the plant canopy for the vegetative stage of plant growth and higher (away from the canopy) during the flowering stage of the plant.
Where should grow lights be placed?
For seedlings, LED grow lights should generally be mounted between 24-36 inches above the plant canopy – however, this depends on the power (wattage) of the light source. Place LED grow lights farthest from the seedlings (~36 inches) – this keeps heat and light intensity low and helps prevent the seedlings from drying out. Once the root system is established and buds begin to sprout, the lights can be moved closer (usually within the first 2-3 weeks).
During the vegetative stage, LED grow lights should be 12-24 inches from the top of the canopy. During this stage, photosynthesis requires more light, so the light source should be located close to the plant.
As the plant enters the flowering stage, the need for strong light decreases. The top leaves of the canopy should be 18-24 inches from the light source to produce flowers. It is during this stage that the plant increases in height and produces fruit. Depending on the light and how you want your crop to grow, it is not necessary to change the height of the light during flowering, especially if you do not want tall plants.
How far away should LED grow lights be from seedlings?
During the initial stages of growth, seedlings are fragile and require less light intensity. This means that you don’t want to increase the intensity too early, as seedlings thrive on more gentle methods. Depending on the size of the light, you can safely keep the grow light somewhere between 24-36 inches from the top of the soil.
How far away should LED grow lights be from plant cloning tissues
Cannabis cloning is a process where cuttings or cuttings from mature plants are used to grow another plant of the same species. The distance of LED grow lights above clones is different than the height required for seedlings. For clones, they will need intense light to get started. Depending on the light intensity and maturity of the plant, the difference between 14-36 inches from the top of the plant canopy can be huge.
How far away should LED grow lights be used
As plants grow, their needs change. After the vegetative stage is complete, the plant enters the flowering or “blooming” stage. For mature plants, they have become necessary for them to thrive. During the flowering stage, LED grow lights should be located between 16-36 inches from the plant canopy. Moving grow lights closer will increase light intensity, maximizing photosynthesis. However, if grow lights are too close above the plants, they can cause the growth to spread, spread, or even damage the plants.
What about other growth stages?
Depending on each stage of growth, plants require different levels of light. To understand exactly how far away a plant should be from a grow light, it’s important to consider the different stages of growth. It’s also important to consider the power output of the grow light – this is often related to the power of the light source, and is a major factor in determining the optimal distance of the LED when beginning the growing process.
Plant growth can be broadly divided into three stages – the nursery, vegetative, and flowering stages.
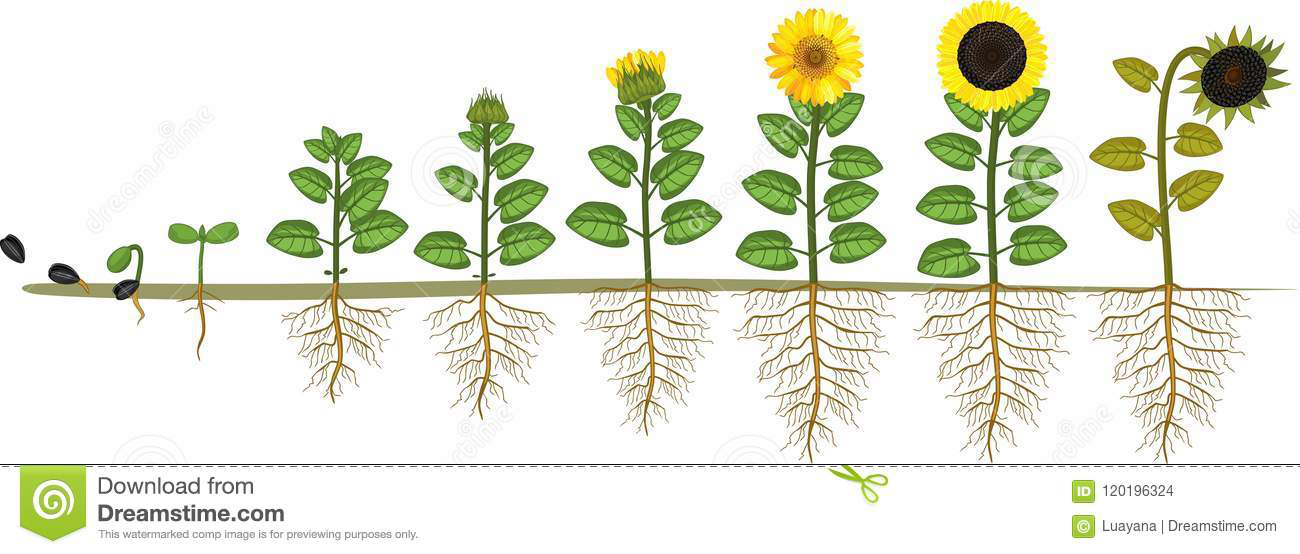

This means that once healthy roots are firmly established, it’s time to increase the intensity and lower the light.
Seedling Stage
During the initial stages as seedlings, LED grow lights should be positioned from above the plant to prevent the soil from drying out.
Some growers may try to blast seedlings with high-intensity light to encourage faster growth, however, this will not help until the plant is established. Seedlings are too fragile at this early stage and require a more gentle approach. Once the plant matures, higher light intensities are needed to encourage photosynthesis.
Vegetative Stage
During the vegetative stage, plants respond well to strong light - it is during this period that plants mature and use photosynthesis to grow quickly. To increase light intensity, LED grow lights should be positioned closer to the plant canopy. Strong, healthy stems and roots are key to successfully achieving repeatable yields.
Increasing light intensity can encourage growth during the vegetative stage, but it is important to monitor the plant closely, making sure to watch for undesirable symptoms caused by too much or not enough light.
Flowering Stage
Flowering is the final stage of the plant’s growth cycle - during this period, fruit production and stem growth accelerate. As plant growth transitions from the vegetative phase to the flowering or blooming phase, it is good practice to “phase” this transition. To do this, gradually raise the height of the LED grow light away from the canopy of the plant (using the height recommendations outlined earlier). Monitor the distance closely, keeping in mind the crop height and flowering needs required for your specific plant/crop.
Adverse Effects of Too Much Light
When plants like cannabis receive too much light at any stage, they often exhibit distressing symptoms. Since LEDs don’t emit much heat, the main issue that needs to be closely monitored is any signs of “light burn.” Other side effects associated with grow lights too close to the plant canopy can be discoloration or stunted/irregular growth. Both must be identified quickly, and the height of the grow light adjusted accordingly.
Signs of mild burn in cannabis plants include leaves that point upward and what is known as “bleaching.” Bleaching is a white or yellow discoloration on the leaves closest to the light. Mild burn can also be identified when the veins of the plant turn green while the rest of the leaves turn yellow.
Increased Light Distance – Cannabis vs. Other Plants
The use of LED grow lights for cannabis production is becoming more common as growers move crop production indoors. LEDs also offer benefits to growers because they can utilize specific light spectra to provide more targeted lighting conditions for different crops. Other benefits when considering LED grow lights include lower power consumption, lower forward heat, and increased yields in a shorter period of time compared to traditional light sources.
The increased distance of light should reflect the height and plant uniformity that growers desire, with a spread of leaves and healthy flowers. If we look at the crop needs of salad greens or lettuce compared to cannabis, we see that salad greens and lettuce are suited to short, more widespread growth, while cannabis is better suited to taller, narrower growth.
Regardless of the crop you are working with, farmers and cannabis growers want the highest quality yields in a shorter growing cycle.
Lighting Distance of Traditional Grow Lights
Before LEDs became popular for indoor growing applications, traditional high-intensity discharge lamps (HIDs) such as high pressure sodium (HPS) and metal halide, as well as fluorescent lamps were widely used. Historically, these lights have been much cheaper to purchase than LED grow lights, and therefore more affordable to use by large indoor growers.
HID or fluorescent lights should be mounted at a greater distance from the plant canopy than LEDs. This is partly because they dissipate more forward heat than LEDs, but they are also only available in a few different wattages/light outputs. The mounting distance of grow lights varies for each stage of growth and depends on the wattage of the grow light being used.
While traditional grow lights have a lower initial cost (lower purchase price), they require more maintenance over time - bulbs need to be replaced and/or cleaned more frequently - and they have significant limitations in lighting control - many lights will not dim and may take a long time to turn on to full light output.
Fluorescent Lights
There are three (3) basic types of fluorescent grow lights - T5, T12, and compact fluorescent. To achieve different light intensities, growers must adjust the height of the plant canopy lights accordingly. One of the advantages of fluorescent lights is that they are difficult to ignite because they do not dissipate enough heat. Regardless, light intensity and heat should always be closely monitored.
For young plants, about 6-12 inches is a reasonable height to start with, as they require higher light intensities. As they mature from vegetative to flowering, it’s wise to double this distance to 12-16 inches. In general, with T5s, it’s best to keep them as close as possible, but monitor for overheating or drying out.
HID Grow Lights (Metal Halide and High Pressure Sodium – HPS)
Metal halide (MH) lights provide a lot of blue light – a spectrum considered best for the vegetative growth stage (3). High pressure sodium (HPS) lights are ideal for growing and flowering plants. Both produce more heat than LEDs, but are relatively inexpensive to purchase.
One way to test HID heat is with the back of your hand. This can help you determine the correct grow light distance. Simply place your hand over the top of the canopy and hold it there for 30 seconds. Your hand should get warm, but not unbearable. If this happens, increase the grow light distance above the plant.
Many commercial growers using 1000W HID lighting typically see heights of 19-26 inches when starting out. From here, they can gradually move closer.
However, because HIDs generate a lot of heat, it is important to avoid heat burns, which can damage any plant. Also, because of the higher heat emitted by HID lights, indoor ventilation is very important.
With over 10 years of collective experience and expertise, Pantech is at the forefront of LED grow lighting solutions and continues to innovate and move the industry forward. Pantech's biologically advanced and research-based approach to LED grow lights leads the industry as we build superior full-spectrum LEDs that make plants stronger and more productive from seed to maturity.
Using 50% less electricity and generating 50% less heat than HPS, our GLMX grow lights provide your plants with up to five years of natural light. The GLTW Series LEDs offer an optimized spectrum that delivers outstanding results right out of the box. We continually support our partners in LED integration, so our grow lights are easy to install and effortless to maintain.