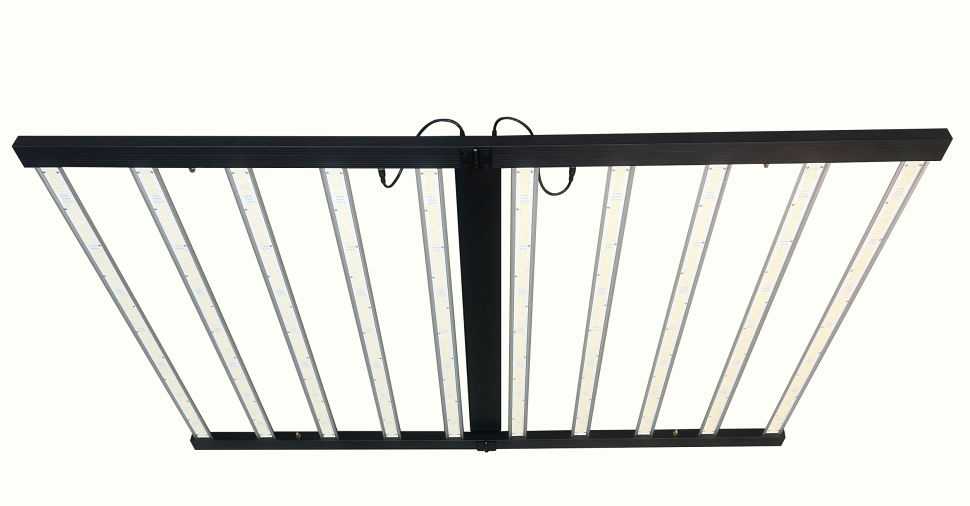
The growth of all things depends on the sun. Without the sun, it depends on supplementary light.
What we need to know is that the growth rate of plants depends on the light intensity, that is, the amount of light radiation energy absorbed by the plant surface, and does not depend on the number of light sources. Many people ask, what is the significance of internal lighting in a greenhouse, how to do it, and what kind of light source should be used?
Plant growth lamps are special lamps that require sunlight according to the laws of plant growth. Plant growth lamps use the principle of sunlight. Light replaces sunlight to provide an environment for plant growth and development.
The following are the light source ratio parameters required for 14 common vegetables:
(1) Lettuce: The red and blue light sources of 6:1 and 7:1 respectively for planting and seedling cultivation are most suitable for its growth.
(2) Leeks: The mass ratios of leek plant height, stem diameter, leaf width, etc. under the red/blue 7:1 treatment were significantly higher than those under other treatments.
(3) Cucumber: 7:2 is the best ratio of red and blue light suitable for the growth of cucumber seedlings, and 7:1 is the best ratio during the growth period.
(4) Green vegetables and water spinach: 7:1 is the best red and blue light ratio suitable for the growth of green vegetables and water spinach leaves.
(5) White radish: The most suitable light quality for growth: red and blue light ratio 8:1.
(6) Lettuce: The ratio of red and blue light is 9:1, which is beneficial to the growth of Lettuce.
(7) Strawberries and tomatoes: Red and blue light 9:1 is most beneficial to the growth of strawberries and tomatoes, and the fruits are plump and nutritious.
(8) Holly: Red and blue light are configured in a ratio of 8:1. Holly grows best, is strong and has a very developed root system.
(9) Sprouts: The red, green and blue light ratio of 6:2:1 has the most obvious effect.
(10) Calla lily: For growth, the ratio of supplementary red and blue light of 6:2 is best.
(11) Anthurium Sun: Comprehensive analysis, red and blue light 7:3 treatment is better, which is beneficial to morphology, root growth and dry matter accumulation.
(12) Dendrobium officinale: Red and blue light 7:3 has the best proliferation effect; 6:4 is more conducive to photosynthesis and material accumulation of seedlings.
Many friends say that the effect of fill light is not good. In fact, a large part of it is due to the wrong way of using the lights. The fill light is not meant to be turned on indoors for more than 10 hours, or to be turned on unexpectedly for a few hours outdoors at night, or to be turned on 24 hours a day. The correct method of use is judged according to the lighting time of the crop. Solanum fruits in greenhouses need 12-14 hours of light during the flowering and fruiting period. In winter, the sunshine time in the north is 5-7 hours. We use laser plant growth lights to supplement the missing light time to increase crop yields. Disease reduction effect. The nighttime supplementary light of laser plant growth lights consists of three stages, the supplementary light stage, the absorption stage and the dark stage.
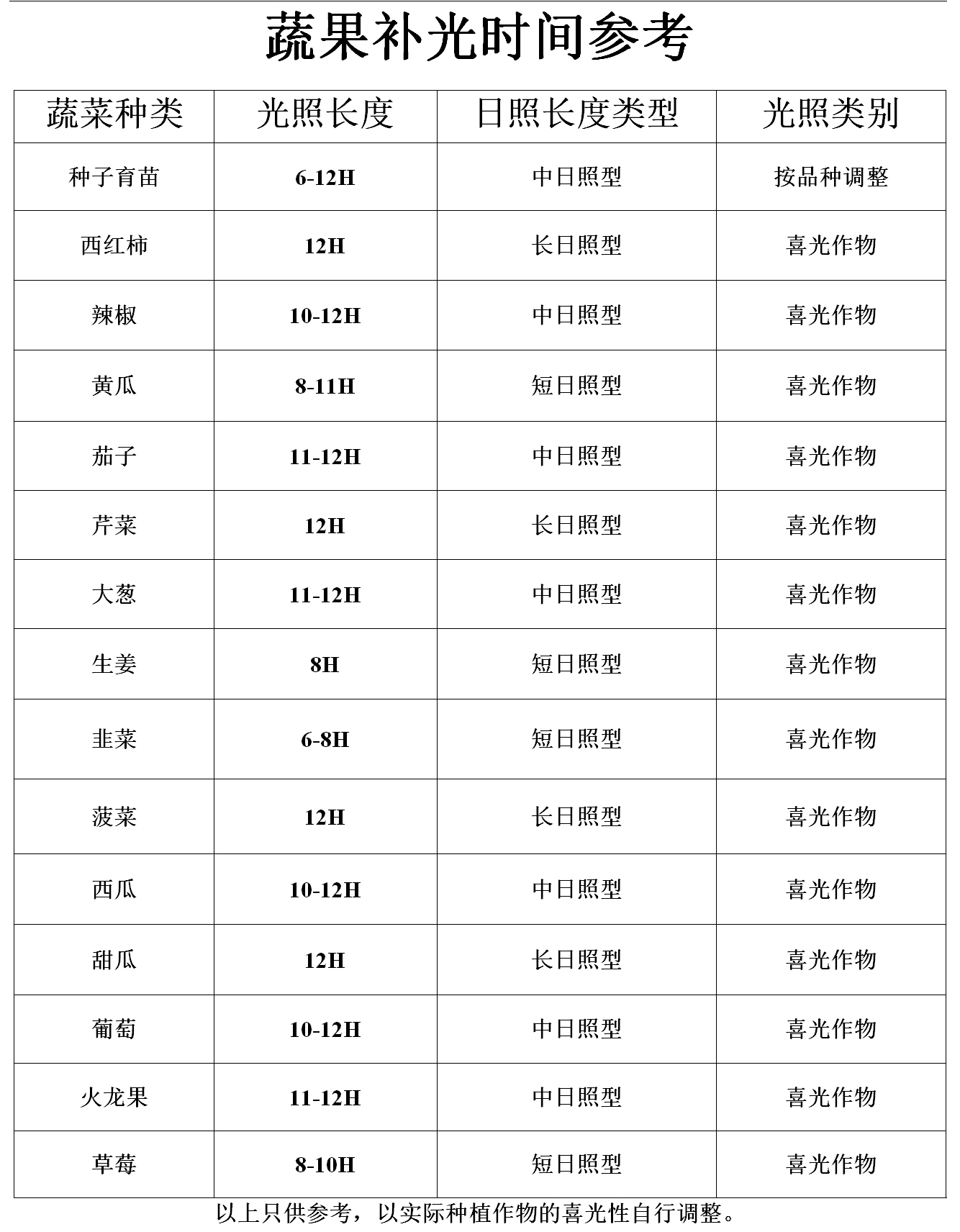
Plant supplementary light time reference
What we need to know is that the growth rate of plants depends on the light intensity, that is, the amount of light radiation energy absorbed by the plant surface, not the number of light sources. Many people ask, what is the significance of greenhouse internal lighting, how to do it, and what kind of light source should be used? The significance of greenhouse internal lighting is to extend the light intensity enough in a day. It is mainly used to grow vegetables, roses and even chrysanthemum seedlings in late autumn and winter. Greenhouse lighting has a huge impact on the growth period and seedling quality. Artificial lighting is necessary on cloudy days and days with low light intensity. At least 8 hours of light per day should be given to crops at night, and the light time should be fixed every day. However, the lack of rest time at night can also cause plant growth disorder and reduce production.
Because the greenhouse frame and covering materials block light, the light intensity in the greenhouse is significantly lower than that in the open field.
Generally, at a height of 1 meter from the ground, the light intensity in the greenhouse is only about 70% of that in the open field. The newness of the agricultural film will also affect the light intensity. Cleaning the water droplets and dust on the greenhouse film has a great impact on the lighting conditions in the greenhouse. According to observations, a layer of water droplets attached to the greenhouse film can reduce the light transmittance by 20-30%; after the new film is used for 2 days, 10 days, and 15 days, the light in the greenhouse can be reduced by 14%, 25%, and 28% respectively due to dust contamination. The light transmittance in the greenhouse varies greatly at different times of the day. It reaches the highest level at noon.
The light intensity in the greenhouse is strong on the top and weak on the bottom; the higher the shed, the weaker the light intensity near the ground. This vertical distribution of light intensity in the greenhouse is also affected by the humidity in the greenhouse, the type of vegetables, height, density, and leaf morphology.
For the horizontal light intensity in the greenhouse, the light intensity on the east side of the greenhouse is greater than that on the west side in the morning for a greenhouse extending from north to south, and vice versa in the afternoon, but the difference in light intensity on both sides of the greenhouse throughout the day is not large. For a greenhouse extending from east to west, the difference in light intensity on both sides of the greenhouse throughout the day is more than 20%.
Reasonable combination of planting When planting different varieties of vegetables in plastic greenhouses, they should be reasonably configured according to the principle of "high in the north and low in the south"; in addition, strengthening cultivation management is also conducive to improving the lighting conditions in the greenhouse; it is reported that the cucumber rack adopts the method of tilting the front row to the south, standing the middle row, and leaning to the north, which can increase the light utilization rate by about 10%.
The sunshine time in the greenhouse is affected by weather conditions and operation and management in the greenhouse. The shortening of the light time in the greenhouse significantly affects the growth and development of vegetables, such as the photosynthesis time, the early and late differentiation of flower buds, or the occurrence law of male and female flowers.
The light intensity is weak and the light time is short on cloudy days and haze days. Because the greenhouse uses covering insulation, and it is often covered early in the afternoon and uncovered late in the morning, the light time in the greenhouse is much less than that in the open field.
In the same region and specific season, the composition of the spectrum in the greenhouse changes with the type of covering film.
Generally, the transmittance of ultraviolet light in greenhouses is low, but in greenhouse production, if there is a lack of ultraviolet light, it will affect the accumulation of crop dry matter, the plants will grow too long, and the content of quality components (such as vitamin C) will be lower than that in the open field. Infrared rays are conducive to the increase of plant and soil temperature, which is very important for winter protected production.
The requirements for light in greenhouses are, first, to maximize the light transmission, and second, to have a large light receiving area and uniform light distribution. From these two aspects, the following measures can be taken to improve the light conditions in the greenhouse.